tRIBS Distributed Hydrologic Modeling System
The TIN-based Real-Time Integrated Basin Simulator is a fully-distributed, continuous hydrologic model operating on a Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN). The code can be accessed through GitHub at tRIBS Distributed Hydrologic Modeling System. This document is intended to serve as a user manual for the tRIBS model, including instructions on how to obtain, compile, set up and run tRIBS using GitHub. In addition, an effort has been made to document the model software design using class and workflow diagrams. Additional information can be obtained through the tRIBS References.
The tRIBS model in this release under the MIT license includes:
Hydrologic Processes:
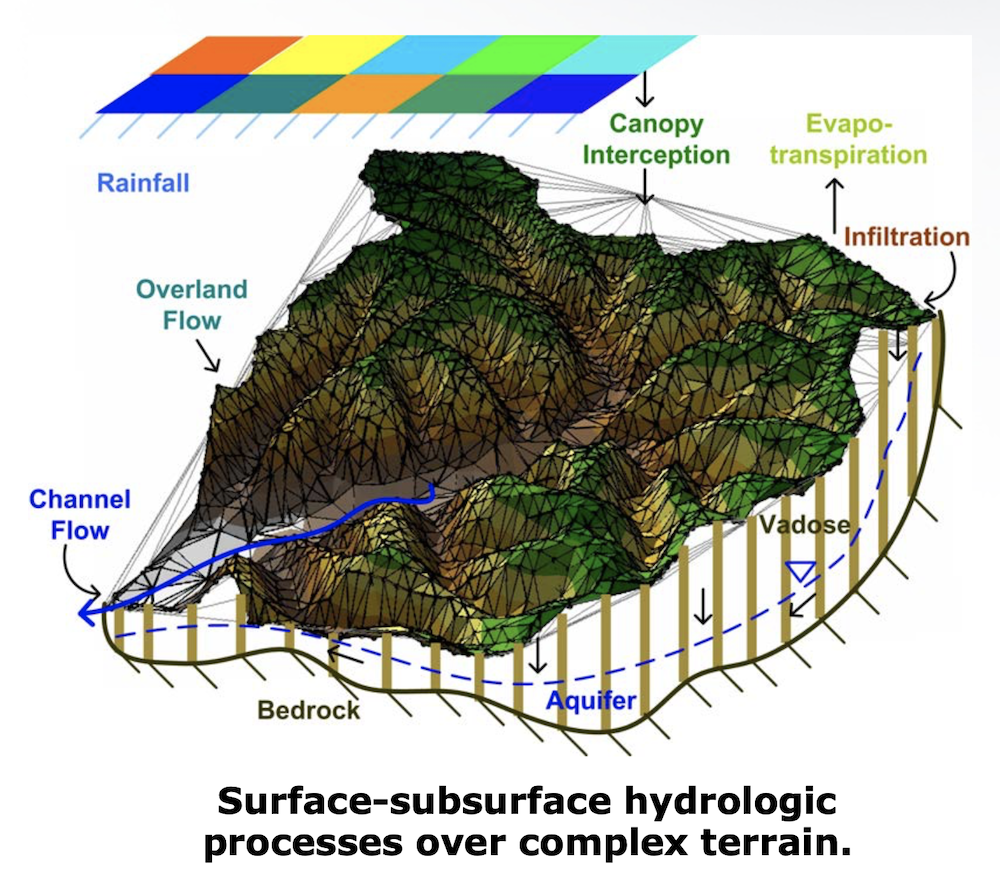
Soil moisture infiltration fronts and their vertical redistribution.
Coupled dynamics of the vadose and saturated zones with a dynamic water table.
Topography-driven lateral fluxes in the vadose and saturated zones.
Radiation and energy balance components on complex terrain.
Single layer snowpack accumulation, ablation and melt on complex terrain.
Rainfall and snow interception on vegetation canopies.
Evaporation of intercepted rainfall, soil evaporation and plant transpiration.
Hydrologic hillslope routing, hydraulic routing in channels, level-pool reservoir routing.
Computational Processes:
Multi-resolution domain generated with channel network and watershed boundary.
Computationally-efficient methods for infiltration, snow dynamics and flow routing.
Serial operation for point-scale simulations and small watershed domains.
Parallelized operation for large domains optimized through subbasin partitioning methods.
Ingestion of time-varying meteorological forcing from stations or raster-based products.
Ingestion of soil and vegetation parameters from tabular data or raster-based products.
Pre- and post-processing workflows for time series and spatial analysis using Python.
ABOUT
DOCUMENTATION
- 1. Model Design
- 2. Model Input Formats
- 3. Model Parameters and Forcings
- 4. Model Input File
- 4.1. Input File Contents
- 4.2. Input File Options
- 4.2.1. Model Run Parameters: Time Variables
- 4.2.2. Model Input Files and Pathnames: Mesh Generation
- 4.2.3. Model Run Parameters: Routing Variables
- 4.2.4. Model Run Parameters: Hydrologic Processes
- 4.2.5. Mesh Input Files and Pathnames: Spatial Data
- 4.2.6. Mesh Input Files and Pathnames: Meteorological Data
- 4.2.7. Mesh Input Files and Pathnames: Output Data
- 4.2.8. Model Modes: Rainfall Forecasting Mode
- 4.2.9. Model Modes: Stochastic Rainfall Mode
- 4.2.10. Model Modes: Restart Mode
- 4.2.11. Model Modes: Parallel Mode
- 5. Model Execution
- 6. Model Outputs
DEVELOPMENT